@cfry said:
The problem that arise is that when I start to improvise I kind of "break the (your) concept". And I would like to avoid ending up in another patch that is so messy that I can not use it if I bring it up after a half a year or so. Lets continue working on it!
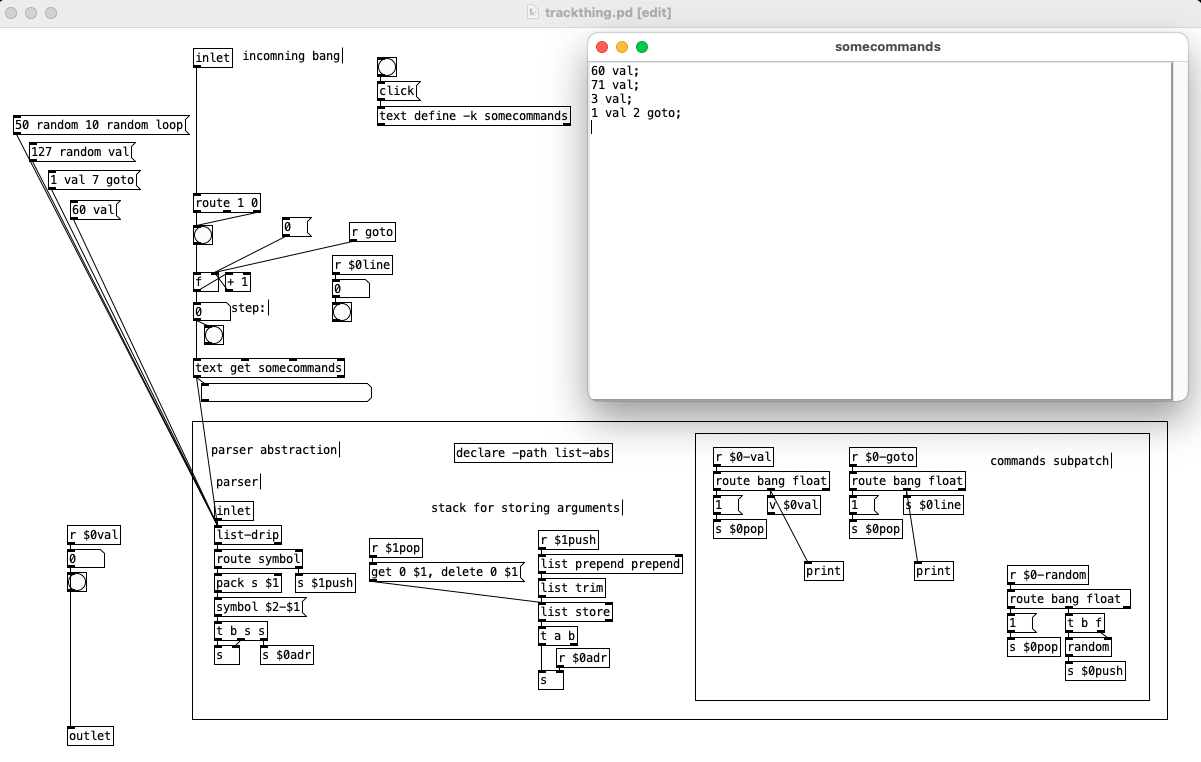
You are definitely getting parts of it and seeing how to develop it but there are parts you don't quite have yet and I can't quite identify what those are so I can explain things. I made a sizable patch that adds a lot of commands but last night I realized I went to far and it would probably confuse things for you, so I will reduce it down to just the things you mentioned, I will follow your lead.
Passing the text name as an argument is just a matter of using your dollar arguments, [text get $1], but you will want to tweak your input for text symbols some.
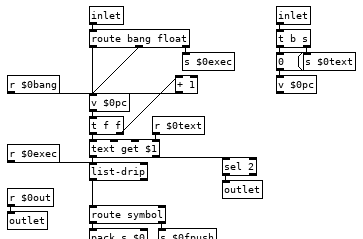
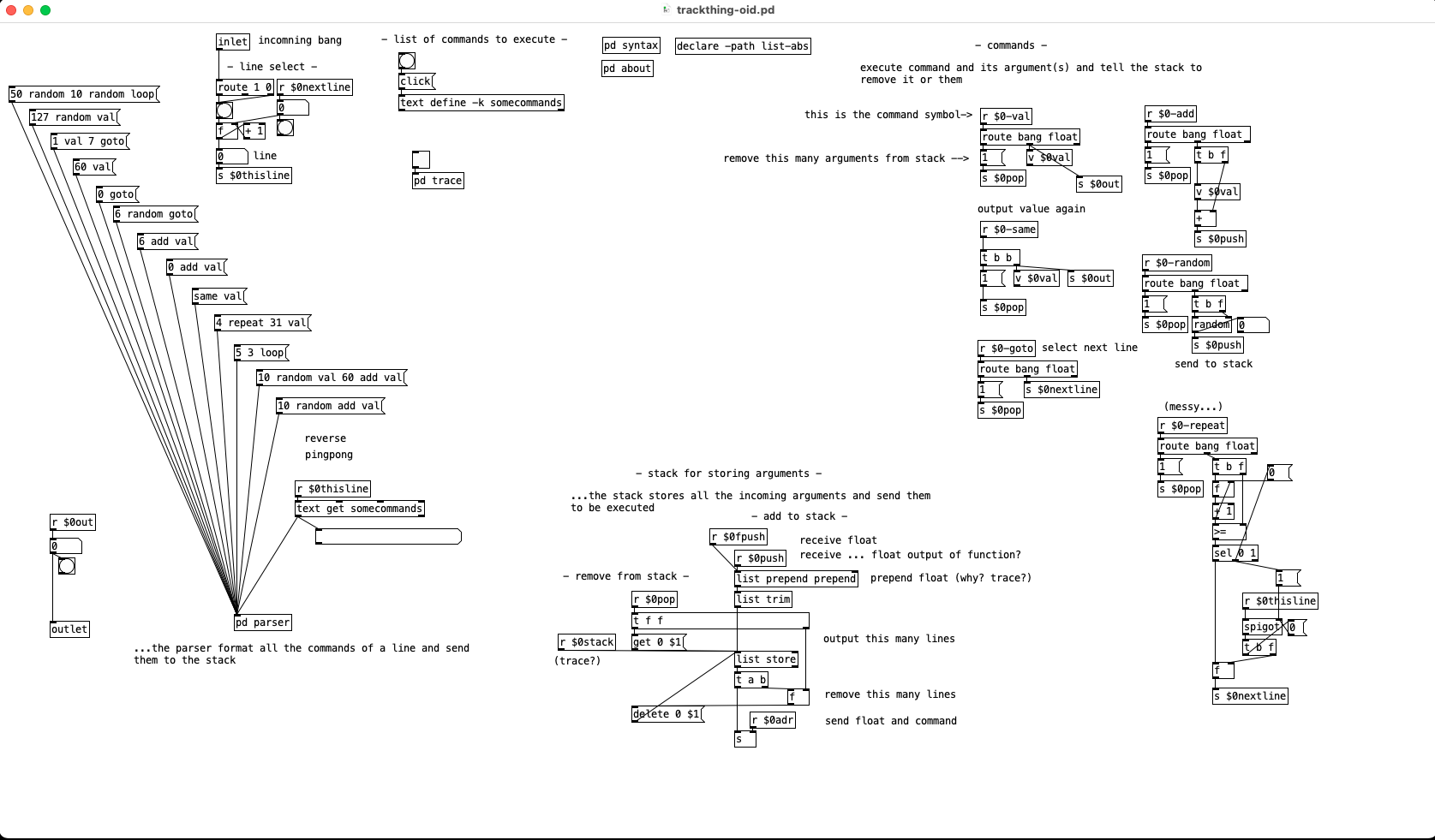
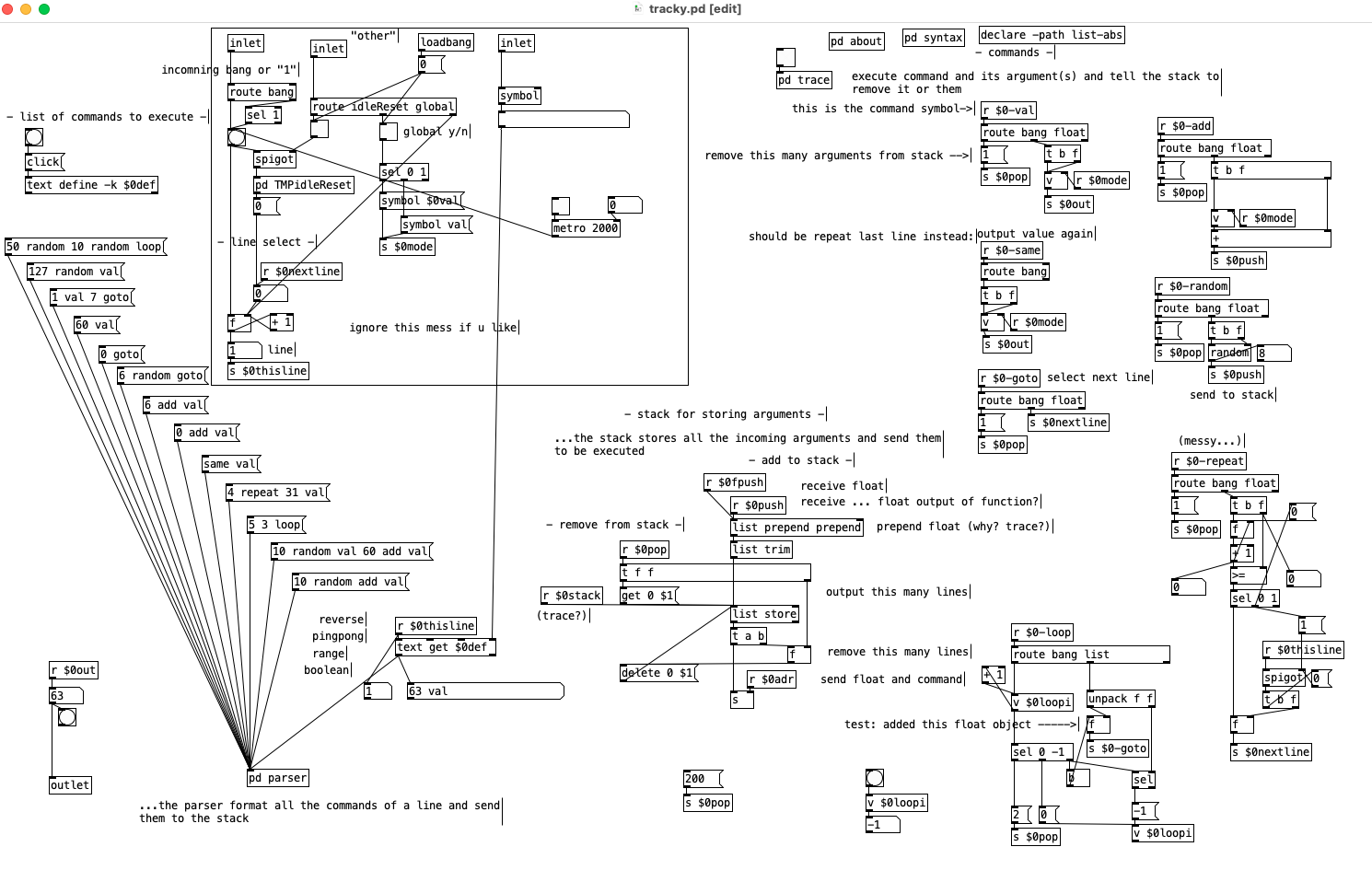
So our right inlet for text symbols goes to a send now so we can easily access that text anywhere in the patch, like in our commands, and we also reset the counter which uses a value for its float for the same reason, we will want to be able to access and change its value from commands. "pc" is short for program counter and it is important that we increment its value before sending a float to the text get otherwise if we change its value in some command it will get overwritten, so having a [t f f] here is almost a must. This also means that [v $0pc] points to the next line to be run and not the one that is currently being run, this is important, fairly useful, and occasionally irksome.
The left inlet has change some as well, we have a [route bang float], bangs and floats go to the counter so we can increment the program or set the next line to be run, the right outlet sends to our [list-drip] which enables us to run commands from the parent patch so when things don't work you can run that print command to print the stack and get some insight or just run commands from a listbox to test things out or whatnot. We also have [r $0bang] on the counter, this lets us increment the counter immediately from a command and start the next line. And finally we have a new outlet that bangs when we reach the end of the text file so we can turn off the metro in the parent patch which is doing the banging, reset the counter to zero, load a new program, or what ever you want to do when the program completes. Middle outlet I did away with, globals can be done as a command, as can most everything.
Variables we can implement with some dynamic patching and a simple abstraction to create the commands for setting and getting the value of any variable.
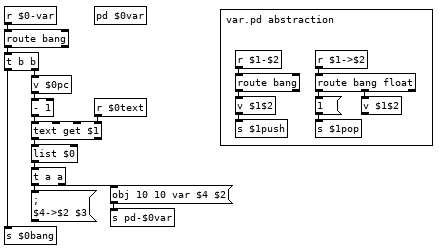
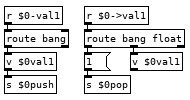
This looks more complicated than it is. If we have the line var val1 10 in our program it runs the var command which bangs [v $0pc] and subtracts 1 from it to get the current line from the text holding our program and then appends our $0 to it giving us the list var val1 10 $0. The first message it goes to creates an instance of the var.pd abstraction in [pd $0var] with the second and fourth elements of the list as arguments, val1 and $0. Second message sends $3 to $4->$2, 10 to $0->val1. To finish off we use that new $0bang receive to bang [v $0pc] so we don't execute the rest of the line which would run val1 pushing 10 to the stack and then push another 10 to the stack. Variable name with a > prepended to it is the command for setting the value of a variable, 22 >val1 in your program would set the value of val1 to 22, val1 would push 22 to the stack. If we could see how pd expands all those dollar arguments in the abstraction it would look like this:
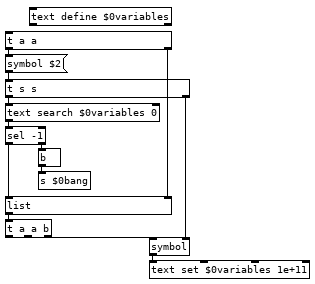
Now you can create as many variables as you would like in your programs and a couple tweaks you can have the abstraction global.pd and subpatch [pd $0globals] so you can have the line global val2 0 and get a global variable that all instances of tracky can read and write from. There are a couple catches, each variable definition must appear on its own line with nothing else after it and with our simple parsing there is nothing to stop you from creating multiple instances of the same variable, if you run the line var val1 10 a second time it will create a second abstraction so when you run val1 it will bang both and each will push 10 to the stack giving you an extra 10 and screw up your program. We can fix this with adding a registry to the var command which searches a [text] to see if it has been created already, something like this after the [list $0] should do it:
And you will want to create a command to clear all variables (and the text if you use it) by sending [clear( to [pd-$0var], or get fancy and add another command in var.pd which bangs [iemguts/canvasdelete] so you can delete individual variables. Using [canvasdelete] has the advantage of not needing a registry for variables, you can just always run ```delete-<variable name>, or what ever you name your delete command, before creating a new variable. Each method has advantages.
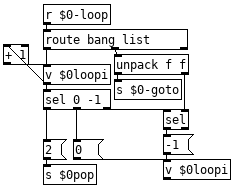
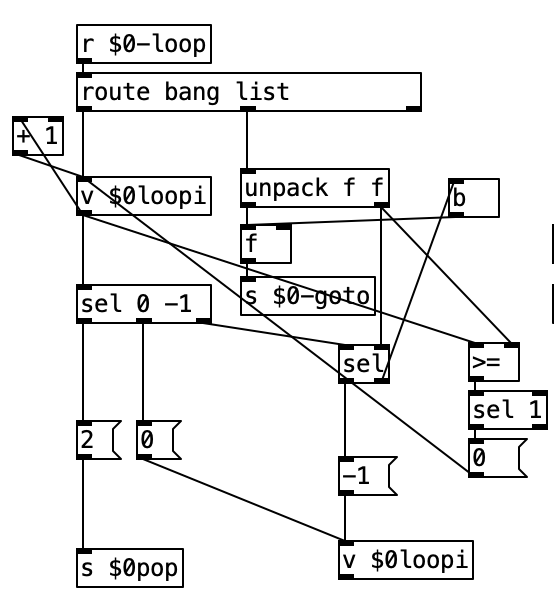
Your loop does not work because the unpack needs to go into the left inlet of the float, that triggers the first loop and causes it to go back, each time the program gets back up to the loop command it increments [v $0loopi] until the select hits the target number of loops which sets $0loopi to -1 which ends the looping.
Not sure what you mean by groups/exclusive groups, can you elaborate or show it with a patch?
None of the above has been tested, but I did think them through better than I did the loop, fairly certain all is well but there might be a bug or two for you to find. Letting you patch them since we think about how things work more when we patch than when we use a patch. Try and sort out and how they work from the pictures and then patch them together without the pictures, following your understanding of them instead of your memory of how I did it. And change them as needed to suit your needs.